test to rule out testicular torsion|testicular torsion manual pdf : inc Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . WEBA CBF divulgou na tarde desta segunda-feira as tabelas das Séries A e B do Campeonato Brasileiro de 2010. E a primeira rodada da Primeira Divisão põe frente a frente os dois .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webAcompanhantes travestis em São José dos Campos reais, profissionais e muito discretas, autênticas deusas viciadas em sexo. Não perca a oportunidade de conhecê-las. Lindas mulheres à espera de sua ligação. Anúncios de travestis em São José dos Campos, perfis de transexuais e shemales. Travestis.
principal medidor de umidade de grãos
testicular torsion signs on examination
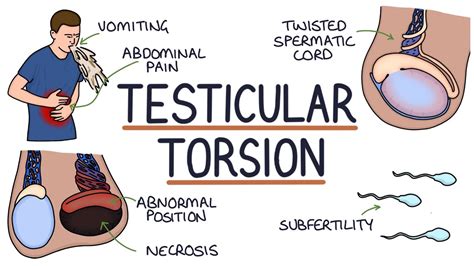
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .
testicular torsion recovery time
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and an.
Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .A testicular torsion occurs when your spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply to your testicle. It requires immediate treatment to prevent permanent damage to your testicle. What is .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in ischaemia of the .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; . In a study of 236 patients with a clinical suspicion of testicular torsion, color-coded Doppler ultrasound had a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 75.2%, and positive and negative predictive values of 80.4% and 100%, .However, pain that has been ongoing for more than 24 hours does not rule out the presence of a testicular torsion. 4, 12 A recent study identified the presence of increasing testicular pain, nausea, vomiting, . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips . The diagnosis of testicular torsion is indeed one of the most important to rule out since it is among the most common diagnoses of emergency physician medical malpractice cases in this age group . Testicular torsion is a difficult diagnosis to rule out based on history and physical examination.
"If there's any concern at all, we recommend a scrotal exam and an ultrasound to rule out torsion," says Dr. Schlomer. How to prevent testicular torsion. While testicular torsion cannot be prevented, being aware of this emergency condition can help prevent permanent damage. Parents should talk to their sons about any pain they may experience in .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, . In addition, CKS notes that a urine dipstick test result may help to rule out an alternative cause for symptoms, such as referred pain from a . Answer: Testicular torsion 1-15. Epidemiology. Bimodal incidence: 1 st year of life and teenage years . is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history and exam. In the United States, approximately 96% of groin hernias are inguinal hernias, about 20% of which are bilateral. 1 Femoral hernias comprise the remaining 4% of groin hernias and are more common in .
Testicular torsion typically causes rapid onset of severe scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting, followed by scrotal edema and induration. Neither urinary frequency nor fever rules out testicular torsion, but the cremasteric reflex is usually absent. Testicular torsion is a time sensitive, . Examination of the spermatic cord for twisting increases the false negative rate improving the utility of ultrasound to rule out the diagnosis; Ultrasound Images of Torsion. Right Testicle with Decreased Flow on Color Doppler - www.ultrasoundcases.info . Tests that can be used to diagnose torsion include: urine tests, which look for infection; . They can rule out testicular torsion or help you obtain any necessary treatment.Ultrasonography is helpful to rule out testicular torsion, but if results are inconclusive, a surgeon should explore the scrotum. 1. . with a testicular mass, laboratory test-
Other tests that can help confirm an infection: Blood and urine tests (e.g., cytology test) that check for infection. Sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening to test for bacteria and other microbes; Ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion or tumors and to look for an enlarged, thickened epididymis; Epididymitis Treatment Options
Create Personal Test Create Group Test . if testicular torsion is suspected but not confirmed with physical exam and history. . Studies. Urinalysis. to rule out epididymitis . Diagnostic criteria. diagnosed by history and physical exam. diagnosis confirmed only during surgery. Differential.Other tests that can help confirm an infection: Blood and urine tests (e.g., cytology test) that check for infection. Sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening to test for bacteria and other microbes; Ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion or tumors and to look for an enlarged, thickened epididymis; Epididymitis Treatment Options
In its acute form, scrotal pain is a medical emergency requiring prompt attention to rule out testicular torsion. The physical exam must include a careful evaluation of the abdomen and inguinal region and a genital exam to assess possible herniation [ 1 , 2 , 3 ].Anatomy of the normal testis, bell clapper anomaly and intravaginal testicular torsion. Blue testis, Green epididymis, Lavender spermatic cord and vessels, Red tunica vaginalis. Normally, the epididymis extends along the full length of the testis posterolaterally so that the upper and lower poles of the testis are covered and the tunica vaginalis parietal lamina is anchored to the .Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of . Further assessment involves examination of the testes and scrotum, STD screenings, urine and blood tests, and ultrasound imaging. An important differential diagnosis is testicular torsion (twisting), which requires emergency surgical intervention. . In uncertain cases, surgery may be performed to further explore the area and rule out .
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. . But ultrasound doesn't always detect the reduced blood flow, so the test might not rule out testicular torsion. Surgery. Surgery might be necessary to determine whether your symptoms are caused by testicular torsion or another .Testicular torsion causes your testicle to twist and cuts off its blood supply. It causes severe pain and requires emergency care. . What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal ultrasound is a quick .
testicular torsion physical exam findings
This large inconsistency makes it unsuitable as an adequate screening or diagnostic test. On gray-scale sonography, in acute phase of torsion, within 1–6 h, testis . It can reliably rule out testicular torsion and helps in clearing clinical dilemma between torsion testis and epididymo-orchitis, and thus help in avoiding unnecessary surgical .
testicular torsion nice guidelines
In some medical centers, all patients with acute scrotum are surgically explored to rule out testicular torsion (5, 6). There is clinical guidance in this regard, . The association between variables and presence of testicular torsion was studied using Chi-square or student t test. Binary logistic regression analysis was done on variables with . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Purpose Testicular torsion requires emergency surgery; thus, prompt and correct diagnosis is very important. Ultrasound with color Doppler is usually the first-choice modality for diagnosis; however, skill and experience are required for confident diagnosis. Recently, contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of testicular torsion has been reported, but there have .
Imperative to rule out testicular torsion in a patient presenting with acute scrotum High index of suspicion on the part of the physician is needed Scrotal Doppler ultrasonography is the imaging study of choice (Am Fam .
principal medidor de umidade de grãos dieletrica
Acute scrotum refers to sudden onset scrotal pain and/or swelling. This must be evaluated immediately to rule out a surgical emergency [2, 3]. 1. Differential diagnoses (Fig. 1) a. Testicular torsion: All acute scrotum presentations should be considered testicular torsion until proven otherwise. b. Appendix testis/epididymis torsion. c . - Rule out perineal necrotizing fasciitis - Ultrasound to evaluate for testicular torsion; Subsequent evaluation . This topic also addresses the clinical management of testicular torsion. Further detail on evaluation and management of necrotizing fasciitis and acute epididymitis are discussed separately. Traumatic injury to the male external .
principar medidor de umidade de grãos
WEBJulia Sandoval. SimpCity OnlyFans 1 Instagram. Follow Discuss. 17 Media. 1 Likes. Photos. Videos. Check out our collection of exactly 17 leaks from Julia Sandoval.
test to rule out testicular torsion|testicular torsion manual pdf